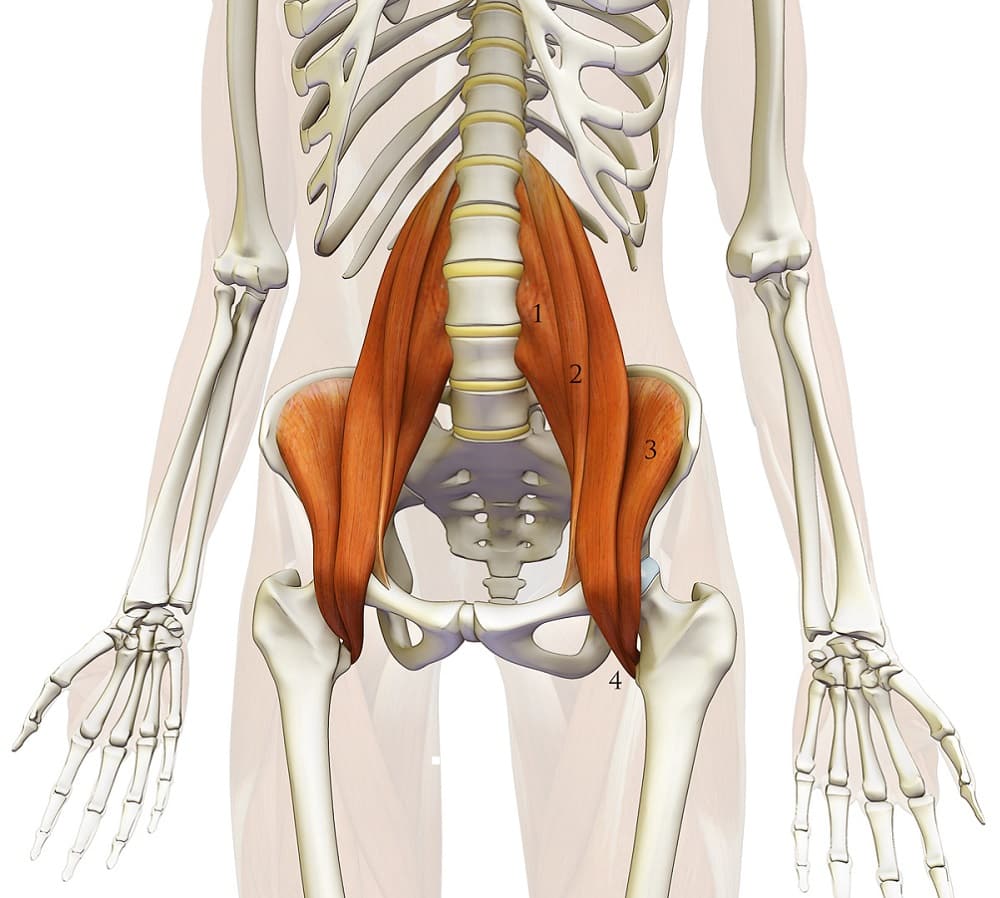
It has been my experience that the Iliopsoas muscle is a major contributor to chronic back pain and it can be quite debilitating. The psoas major is a deep-seated core muscle connecting your lower spine to your upper thigh. When it’s tight or dysfunctional, it can contribute to a range of issues, including back pain. The muscle shortens when you sit so it is very common in office workers. Its amazing the amount of time we spend sitting……drive to work, sit at the job, lunch, drive home, sit to have dinner, sit watching the the Leafs getting eliminated in the playoffs again (well maybe there is a lot of standing and screaming at the TV also). Typically what happens is the muscle “learns” to be short(and usually weakens) and as you start to move more (weekend activities) it tugs and pulls on the lower back. This can irritate the facet joints, discs and create a muscular imbalance over time. If this injury is not addressed it can contribute to chronic recurrent lower back pain as well as nerve and disc injuries.
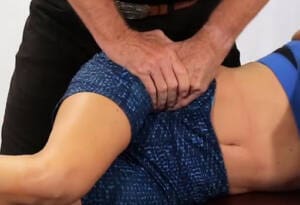 Active Release is one of the best ways to restore motion help lengthen the muscle.
Active Release is one of the best ways to restore motion help lengthen the muscle.
Here are some steps you might consider:
- Stretching: Gentle stretches targeting the psoas muscle can help alleviate tension. Lunges, pigeon pose, or even simply kneeling and leaning back can provide relief.
- Strengthening: Strengthening exercises for the core muscles can help stabilize your spine and take some of the strain off the psoas. Planks, bridges, and leg lifts are good options.
- Massage or Myofascial Release: Getting regular massages or using techniques like foam rolling can help release tension in the psoas and surrounding muscles.
- Posture Awareness: Pay attention to your posture throughout the day. Poor posture can contribute to tightness in the psoas and exacerbate back pain.
- Professional Help: Consider seeing a chiropractor who specializes in back pain. They can provide personalized exercises and treatments to address your specific issues.
- Heat and Ice Therapy: Alternating between heat and ice packs can help reduce inflammation and relax tight muscles.
- Mind-Body Practices: Practices like yoga or tai chi can help improve flexibility, strength, and body awareness, all of which can contribute to reducing back pain.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: If your back pain is aggravated by sitting for long periods, consider ergonomic adjustments to your workspace or investing in a supportive chair.
- Pain Management: In severe cases, pain management techniques like medication or injections may be necessary. However, these should be used cautiously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Remember, consistency is key. Incorporating these strategies into your daily routine can help manage chronic back pain associated with the psoas muscle. However, it’s essential to listen to your body and not push through pain, as this can exacerbate the issue.


